What Is Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
Overview
Dysfunction of the tibialis posterior tendon is a common condition and a common cause of acquired flatfoot deformity in adults. Women older than 40 are most at risk. Patients present with pain and swelling of the medial hindfoot. Patients may also report a change in the shape of the foot or flattening of the foot. The foot develops a valgus heel (the heel rotates laterally when observed from behind), a flattened longitudinal arch, and an abducted forefoot. Conservative treatment includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, rest, and immobilisation for acute inflammation; and orthoses to control the more chronic symptoms. Surgical treatment in the early stages is hindfoot osteotomy combined with tendon transfer. Arthrodesis of the hindfoot, and occasionally the ankle, is required in the surgical treatment of the later stages of tibialis posterior dysfunction. 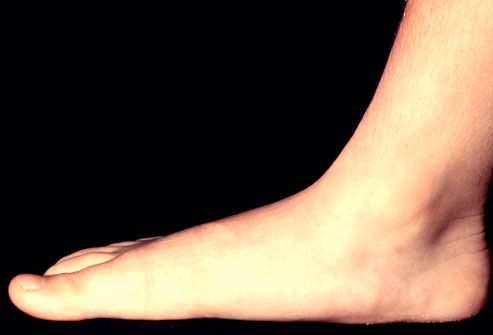
Causes
Women are affected by Adult Acquired Flatfoot four times more frequently than men. Adult Flatfoot generally occurs in middle to older age people. Most people who acquire the condition already have flat feet. One arch begins to flatten more, then pain and swelling develop on the inside of the ankle. This condition generally affects only one foot. It is unclear why women are affected more often than men. But factors that may increase your risk of Adult Flatfoot include diabetes, hypertension, and obesity.
Symptoms
Not everyone with adult flatfoot has problems with pain. Those who do usually experience it around the ankle or in the heel. The pain is usually worse with activity, like walking or standing for extended periods. Sometimes, if the condition develops from arthritis in the foot, bony spurs along the top and side of the foot develop and make wearing shoes more painful. Diabetic patients need to watch for swelling or large lumps in the feet, as they may not notice any pain. They are also at higher risk for developing significant deformities from their flatfoot.
Diagnosis
Starting from the knee down, check for any bowing of the tibia. A tibial varum will cause increased medial stress on the foot and ankle. This is essential to consider in surgical planning. Check the gastrocnemius muscle and Achilles complex via a straight and bent knee check for equinus. If the range of motion improves to at least neutral with bent knee testing of the Achilles complex, one may consider a gastrocnemius recession. If the Achilles complex is still tight with bent knee testing, an Achilles lengthening may be necessary. Check the posterior tibial muscle along its entire course. Palpate the muscle and observe the tendon for strength with a plantarflexion and inversion stress test. Check the flexor muscles for strength in order to see if an adequate transfer tendon is available. Check the anterior tibial tendon for size and strength.
Non surgical Treatment
Initial treatment for most patients consists of rest and anti-inflammatory medications. This will help reduce the swelling and pain associated with the condition. The long term treatment for the problem usually involves custom made orthotics and supportive shoe gear to prevent further breakdown of the foot. ESWT(extracorporeal shock wave therapy) is a novel treatment which uses sound wave technology to stimulate blood flow to the tendon to accelerate the healing process. This can help lead to a more rapid return to normal activities for most patients. If treatment is initiated early in the process, most patients can experience a return to normal activities without the need for surgery. 
Surgical Treatment
For more chronic flatfoot pain, surgical intervention may be the best option. Barring other serious medical ailments, surgery is a good alternative for patients with a serious problem. There are two surgical options depending on a person?s physical condition, age and lifestyle. The first type of surgery involves repair of the PTT by transferring of a nearby tendon to help re-establish an arch and straighten out the foot. After this surgery, patients wear a non-weight bearing support boot for four to six weeks. The other surgery involves fusing of two or three bones in the hind foot below the ankle. While providing significant pain relief, this option does take away some hind foot side-to-side motion. Following surgery, patients are in a cast for three months. Surgery is an effective treatment to address adult-acquired flatfoot, but it can sometimes be avoided if foot issues are resolved early. That is why it is so important to seek help right away if you are feeling ankle pain. But perhaps the best way to keep from becoming flatfooted is to avoid the risk factors altogether. This means keeping your blood pressure, weight and diabetes in check.